 The Obama administration is debating a more robust intervention in Syria, including possible U.S. airstrikes, in a significant escalation of its weeks-long military assault on the Islamic extremist group that has destabilized neighboring Iraq and killed a U.S. journalist, officials said Friday.
The Obama administration is debating a more robust intervention in Syria, including possible U.S. airstrikes, in a significant escalation of its weeks-long military assault on the Islamic extremist group that has destabilized neighboring Iraq and killed a U.S. journalist, officials said Friday.
While President Barack Obama has long resisted being drawn into Syria’s bloody civil war, officials said recent advances by the Islamic State group have made clear that it represents a threat to the interests of the U.S. and its allies. The beheading of James Foley, a U.S. journalist, has contributed to what officials called a “new context” for a challenge that has long divided the president’s team.
Officials said the options include speeding up and intensifying limited U.S. efforts to train and arm moderate Syrian rebel forces that have been fighting the Islamic State as well as fighting the government of President Bashar Assad. Another option would be to bolster other partners on the ground to take on the Islamic State, including the Syrian Kurds.
But U.S. officials said they would also take a look at airstrikes by fighter jets and bombers as well as potentially sending special operations forces into Syria, like those who failed to rescue Foley and other hostages on a mission in July. One possibility officials have discussed for Iraq that could be translated to Syria would be a series of unmanned drone strikes targeting Islamic State leaders, much like those conducted in Yemen, Somalia and Pakistan.
Whether Obama would actually authorize a new strategy remained unknown, and aides said he has not yet been presented with recommendations.
Changing minds
The president has long expressed skepticism that more assertive action by the U.S., including arming Syrian rebels as urged in 2011 by Hillary Rodham Clinton, then the secretary of state, would change the course of the civil war there. But he sent out a spokesman Friday to publicly hint at the possibility a day after the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff said the Islamic State could not be defeated without going after it in Syria.
“If you come after Americans, we’re going to come after you, wherever you are,” said Benjamin Rhodes, the president’s deputy national security adviser. “We’re actively considering what’s going to be necessary to deal with that threat, and we’re not going to be restricted by borders.”
U.S. operations against the Islamic State group in Syria would expand the scope and goals of the military intervention Obama ordered in Iraq two weeks ago. At the time, the president said he authorized airstrikes to defend U.S. personnel and prevent the genocide of religious minorities threatened by the Islamic State.
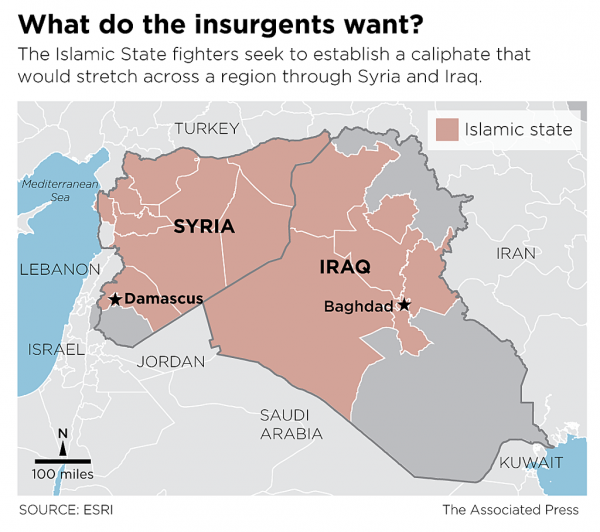
But he has also ordered strikes to help Iraq’s government reclaim control of the vital Mosul Dam from the Islamic State. Sending U.S. warplanes or drones to cross the border into Syria would mean that he was now taking on the mission of degrading or even crippling the Islamic State, which has established what it calls an Islamic caliphate on a wide band of territory across the two countries.
An expanded intervention into Syria would represent a striking turnaround for a president who has opposed such a move before, and some administration officials therefore doubt that he will agree. From the start of the Syrian civil war, Obama’s response has been marked by a pattern of heightened public statements and indications of stepped-up involvement, followed by far less action than suggested.
Backing off
At one point, Obama declared that Assad had to “step aside” and at another he laid down a “red line” against any use of chemical weapons. But the president rejected the 2011 proposal backed by Clinton to arm and train small groups of vetted rebels, fearful that the weapons could fall into the wrong hands.
Just a year ago, he vowed to retaliate against Syria for using chemical weapons on civilians, only to abruptly reverse himself and ask Congress to decide whether to go forward. He then pivoted again to embrace a Russian plan to remove Syria’s chemical weapons without taking military action.
Obama eventually approved a limited effort to arm and train vetted rebels and this summer asked Congress for another $500 million to help, but the flow of aid has been so tightly controlled that some rebel leaders have said it seemed designed less to turn the tide of war than to keep them alive — while creating an impression that the United States is helping.
As recently as two weeks ago, Obama rejected the notion that arming the rebels earlier would have made a difference, saying that has “always been a fantasy.” He said the administration had difficulty finding, training and arming a sufficient cadre of secular Syrians.
What is now under consideration would be a different goal: not to punish Assad’s government or to further his ouster but to cripple the Islamic State. As it happens, that would actually work in Assad’s favor, since the Islamic State has been one of the most effective of the various factions fighting Syrian government forces. But it might be more directly in the interest of the U.S., given the threat posed by an Islamic State caliphate whose brutality was captured in the video image of a masked man beheading Foley.
Dallas News



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.