A huge Chinese Long March 5B rocket booster is falling back to Earth in an uncontrolled descent, with reentry currently expected on early Sunday (May 9), and you can track its fall on one of several websites.
The 23-ton (21 metric tons) core stage likely will fall into an uninhabited area, given that 70% of Earth’s surface is covered by ocean. That said, entities around the world are keeping an eye out just in case — and providing regular updates online.

As of early Saturday, the falling rocket booster was forecast to reenter Earth’s atmosphere over the southern Pacific Ocean on Sunday (May 9) at about 12:19 a.m. EDT (0419 GMT), according to the Aerospace Corp., which is tracking the object.
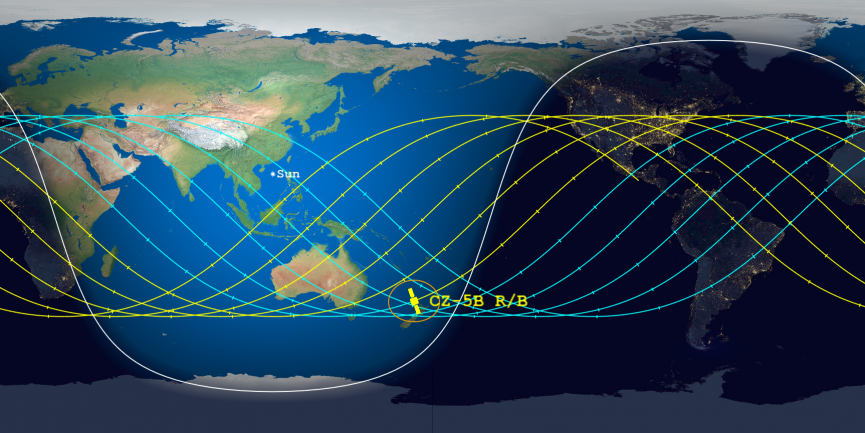
U.S. Space Command is updating space-track.org at least once a day with the latest information about where the rocket is likely to fall, based on parameters such as how high Earth’s atmosphere is billowing and how drag is expected to affect the massive Chinese vehicle.
The Aerospace Corporation, which supports national security space programs, posts regularly on its Twitter feed and occasionally on Medium about the core stage status. More details about re-entry predictions are also available on its website.
Another Twitter feed to keep an eye on is that of Jonathan McDowell, a well-known tracker of uncontrolled falls in the U.S. space community. He’s been posting several times a day about the progress of the Long March 5B.
Amateur skywatchers are also keeping an eye out for the rocket, with the Virtual Telescope’s Gianluca Masi planning to broadcast live footage from Rome if the core stage is visible from there. Weather permitting, that webcast is expected to begin tonight, May 7, at 10:40 p.m. EDT (0240 GMT). You can watch it directly from the Virtual Telescope here and on YouTube.
China has been occasionally commenting on the situation in state media and in news reports, so keep an eye out in English-language coverage for any comments state officials may have.
Alternatively, you might want to look for the new Chinese space station that this Long March 5B helped to build. On April 28, the rocket launched the core stage of the T-shaped Tianhe space station, which will eventually include several modules.
The website (or apps) by Heavens-Above has a list of passes of the Tianhe module tailored for your preferred observation location. In general, it appears the vehicle is bright enough to spot with the naked eye, but you might have better luck with binoculars or a telescope, especially in light-polluted areas.
More technical information on the space station’s orbit is available at NY2O.com, including its perigee, apogee, inclination and period.
SPACE .COM

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.