Even if it were somehow possible to escape eastern Aleppo, Abdullah Shiyani, a 10-year-old boy who dreams of being a doctor, says he wouldn’t leave. It would mean leaving behind too many people who need help.
“We have a lot of injured people here,” he told Reuters over the Internet. “Maybe we can help them.”
His father was a fighter, killed on the frontline. So he lives with his five siblings in a neighborhood that is almost an empty ghost town. They survive off money from a charity, buying potatoes, parsley and onions when they can. Three weeks ago they even had some meat.
Three of his friends were killed in a rocket attack a few months ago. With school long-since closed, he and his other friends spend their days racing through the empty streets, kicking a ball or playing a game called “guns and knives”.
They duck into buildings when the planes fly overhead, he says, because “we know about the machine guns firing from the planes”.
Aleppo, Syria’s biggest city before civil war uprooted half of the country’s population and killed hundreds of thousands of people, is now the conflict’s biggest prize. Opposition-held areas are now under total siege and heavy bombardment as President Bashar al-Assad’s government attempts to deal a death blow to a five year rebellion.
The city has been divided into rebel and government-held zones for years. But recent months have seen government troops, backed by Russian air strikes and Shi’ite fighters from Lebanon, Iran, Iraq and Afghanistan, close in on the rebel zone, where a quarter of a million people remain trapped.
Civilians reached by Reuters over the Internet and telephone tell of a bleak existence amid the ruins — of shortages of food, water and electricity, and incessant fear for their own lives and their loved ones.
“Every day there are about three to four (air) raids close to our house,” said 33-year-old mother-of-one Um Fahd, whose husband, brother and father have all been killed. “Our neighbor’s house was shelled and destroyed. A lot of people have died but we’re still here, thank God.”
She and her son survive on an allowance of $50 a month from a charity, barely enough for food.
“It’s not enough, but we’re grateful for whatever we get,” she said.
In the home she shares with her son, her sister and her sister’s three children, the entire family crams into the sturdiest room in the house whenever they hear warplanes, in the hope it will shield them from bombing.
“When the kids hear the sound of plane, they immediately know that they should go to that room,” she said.
Another woman, Um Ahmed, described how she and her husband careered through gunfire and shelling to flee during a brief window when the siege was broken. When it was reimposed, her two sons and their families remained trapped inside. Her voice trembled as she described her own escape under gunfire.
“I hesitated about leaving. I didn’t want to leave them behind. I haven’t been able to sleep at night, I’m so scared for them, because of the bombardments,” she said.
BROKEN FAMILIES
Aleppo has been one of the Middle East’s great cities for centuries. Its picturesque old center of covered spice markets has long since been reduced to rubble by street fighting. The crisis dramatically intensified earlier this year, when the government side captured territory north of the city, severing a vital supply route to Turkey.
A complete blockade of the rebel-held eastern sector was imposed in July, when pro-government forces severed the last road in. A rebel counter attack, heavily supported by Sunni Muslim jihadist groups, broke the siege in August, but government forces reimposed it in the last few days.
The government-held west of Aleppo holds more people and has also faced increasingly heavy insurgent shelling. But the destruction in the rebel-held east, targeted in daily air strikes, has been far more extensive.
The west came close to being encircled itself during fighting last month as rebels severed the only road in. The advancing government forces secured that route on Friday.
The devastation, death and displacement have left some neighborhoods of the besieged east sparsely populated, residents said. There is little work and no school. Most people spend their days trying to secure enough food to survive, and taking cover when the bombs fall. The children grow up fast.
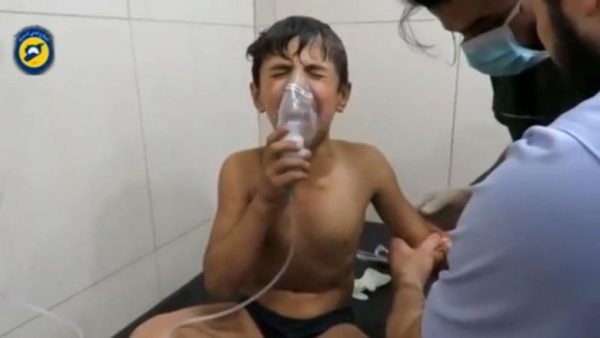
The director of the al-Quds hospital in eastern Aleppo, Dr Hamza al-Khatib, said that during a recent suspected chlorine gas attack, children young enough to remember little other than war appeared to know instinctively how to react.
“I was shocked how five- or six-year-old children were holding oxygen masks alone, without help – like they were grown men who understood that this was the way to relieve their suffering,” he said.
Rescue workers accused the government of carrying out the Sept. 6 chlorine attack. Damascus denied involvement, saying “terror groups” were behind such attacks. The United Nations has blamed the government for previous attacks using chlorine gas.
When people die, relatives take the kids.
“My wife is looking after the five children my son left behind, and I’m helping her,” said 65-year-old Eid al-Ibrahim, whose eldest son was killed in an air strike.
People sometimes have to fight for their food.
“In our neighborhood they sell bags of five bread loaves … organized by the neighborhood council,” Ibrahim said, describing “a lot of crowding and fighting.”
Brita Hagi Hassan, president of the city council for opposition-held Aleppo, said prices had gone up by 10 times due to shortages induced by the siege. He said around 15 to 20 percent of eastern Aleppo’s residents left during the time the siege was lifted.
Many now eat little but lentils and cracked wheat. Electricity from motor generators is available only for three to six hours a day and damage to power facilities has long left eastern Aleppo with no running water.
Opposition-held neighborhoods have long suffered air strikes and attacks with barrel bombs — drums packed with explosives and shrapnel dropped from the air — from the government side.
The United Nations’ Commission of Inquiry on Syria has condemned the bombing of medical facilities in rebel-held districts, which it said were “explicitly targeted for destruction or assassination” of staff.
Damascus denies targeting civilians. A Syrian military source said the aim is to stop rebel shelling of western Aleppo and to encircle the militants in the east.
REUTERS

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.