 A monster black hole powering “the brightest lighthouse in the distant universe” has been discovered that is 12 billion times more massive than the sun, scientists have revealed.
A monster black hole powering “the brightest lighthouse in the distant universe” has been discovered that is 12 billion times more massive than the sun, scientists have revealed.
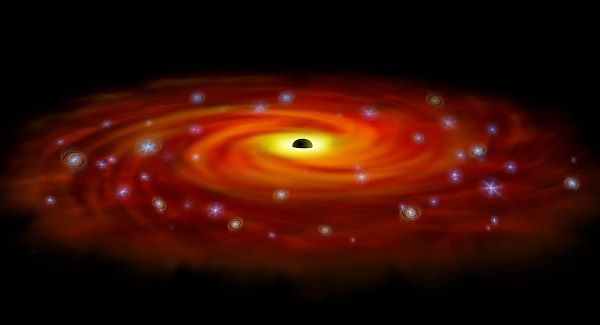
The extraordinary object is at the centre of a quasar — an intensely powerful galactic radiation source — with a million billion times the sun’s energy output.
For years the nature of quasars, discovered in 1963, remained a mystery. Today scientists believe they are generated by matter heating up as it is dragged into supermassive black holes at the centre of distant galaxies.
The new object, named SDSS J0100+2802, is 12.8 —billion light years from Earth and was formed just 900 million years after the Big Bang that gave birth to the universe.
Astronomers cannot explain how such an enormous black hole could have formed so early in cosmic history, soon after the first stars and galaxies emerged.
Dr Fuyan Bian, from the Australian National University, a member of the international team, said: “Forming such a large black hole so quickly is hard to interpret with current theories.
“This black hole at the centre of the quasar gained enormous mass in a short period of time,” he said.
The quasar, the brightest ever detected in the early universe, was found after astronomers conducted a survey of distant luminous objects using data from several large telescopes around the world. It had a “redshift” — a measurement of the stretching of light to the red end of the spectrum by the expansion of the universe — of 6.30, marking it out as a very distant and old object.
Only 40 known quasars have a redshift higher than six.
Irish Examiner

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.