
Saudi Arabia and Iran are at loggerheads. They have long been rivals, but it’s all recently got a lot more tense. Here’s why.
How come Saudi Arabia and Iran don’t get along?
Saudi Arabia and Iran – two powerful neighbours – are locked in a fierce struggle for regional dominance.
The decades-old feud between them is exacerbated by religious differences. They each follow one of the two main sects in Islam – Iran is largely Shia Muslim, while Saudi Arabia sees itself as the leading Sunni Muslim power.

This religious schism is reflected in the wider map of the Middle East, where other countries have Sunni or Shia majorities, some of whom look towards Iran or Saudi Arabia for support or guidance.
Historically Saudi Arabia, a monarchy and home to the birthplace of Islam, saw itself as the leader of the Muslim world. However this was challenged in 1979 by the Islamic revolution in Iran which created a new type of state in the region – a kind of theocracy – that had an explicit goal of exporting this model beyond its own borders.

In the past 15 years in particular, the differences between Saudi Arabia and Iran have been sharpened by a series of events.
The 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq overthrew Saddam Hussein, a Sunni Arab who had been a major Iranian adversary. This removed a crucial military counter-weight to Iranian influence in Iraq, which has been rising since then.

Fast-forward to 2011 and uprisings across the Arab world caused political instability throughout the region. Iran and Saudi Arabia exploited these upheavals to expand their influence, notably in Syria, Bahrain and Yemen, further heightening mutual suspicions.
Iran’s critics say it is intent on establishing itself or its proxies across the region, and achieve control of a land corridor stretching from Iran to the Mediterranean.
How have things suddenly got worse?
The strategic rivalry is heating up because Iran is in many ways winning the regional struggle.
In Syria, Iranian (and Russian) support for President Bashar al-Assad has largely routed rebel group groups backed by Saudi Arabia.
Saudi Arabia is trying desperately to contain rising Iranian influence and the militaristic adventurism of the kingdom’s young and impulsive Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman – the country’s de facto ruler – is exacerbating regional tensions.

He is waging a war against rebels in Saudi Arabia’s southern neighbour, Yemen, in part to stem perceived Iranian influence there, but after nearly three years this is proving a costly gamble.
Meanwhile in Lebanon, many observers believe the Saudis put pressure on the prime minister to resign in order to destabilise a country where Iran’s ally, Shia militia group Hezbollah, leads a politically powerful bloc and controls a huge, heavily armed fighting force.
There are also external forces at play. Saudi Arabia has been emboldened by support from the Trump administration while Israel, which sees Iran as a mortal threat, is in a sense “backing” the Saudi effort to contain Iran.
 Image copyrightEPA
Image copyrightEPAThe Jewish state is fearful of the encroachment of pro-Iranian fighters in Syria ever closer to its border.
Israel and Saudi Arabia were the two countries most resolutely opposed to the 2015 international agreement limiting Iran’s nuclear programme, insisting that it did not go far enough to roll back any chance of Iran obtaining the bomb.
Who are their regional allies?
Broadly speaking the strategic map of the Middle East reflects the Shia-Sunni divide.
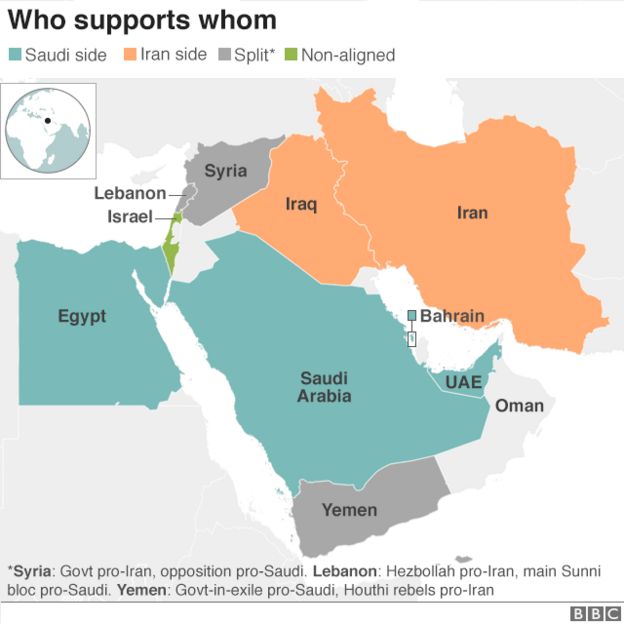
In the pro-Saudi camp are the other major Sunni actors in the Gulf – the UAE, Kuwait and Bahrain, as well as Egypt and Jordan.
In the Iranian camp is Syria’s government, which has been strongly backed by Iran, and where pro-Iranian Shia militia groups, including the Lebanon-based Hezbollah, have played a prominent role in fighting predominantly Sunni rebel groups.
The Shia-dominated Iraqi government is also a close ally of Iran, though paradoxically it also retains a close relationship with Washington on whom it has depended for help in the struggle against so-called Islamic State.
How is the Saudi-Iranian rivalry being played out?
This is in many ways a regional equivalent of the Cold War, which pitted the US against the Soviet Union in a tense military standoff for many years.
Iran and Saudi Arabia are not directly fighting but they are engaged in a variety of proxy wars around the region.

Syria is an obvious example while in Yemen Saudi Arabia has accused Iran of supplying ballistic missiles fired at Saudi territory by the Shia Houthi rebel movement – an incident which heightened the war of words between the two countries.
But having become bogged down in Yemen and essentially defeated in Syria, Saudi Arabia seems to have its eye on Lebanon as the next proxy battlefield.
Lebanon risks being tipped into Syria-like chaos but few analysts see Saudi interests prevailing there.
Conflict in Lebanon could so easily draw in Israel in opposition to Hezbollah and this could lead to a third Israel-Lebanon war far more devastating than any of the previous encounters.
Some cynics wonder if the Saudi crown prince’s game plan is to trigger a war between Israel and Hezbollah and deliver a heavy blow to the group this way!
Are we heading towards a direct war between Saudi Arabia and Iran?
So far Tehran and Riyadh have fought via proxies. Neither is really geared up for a direct war with the other but one successful rocket attack on the Saudi capital from Yemen could upset the apple cart.
One obvious area where they could come into direct conflict is in the waters of the Gulf, where they face each other across a maritime border.
But here too fighting could risk a much broader conflict. For the US and other Western powers, freedom of navigation in the Gulf is essential and any conflict that sought to block the waterway – vital for international shipping and oil transportation – could easily draw in US naval and air forces.
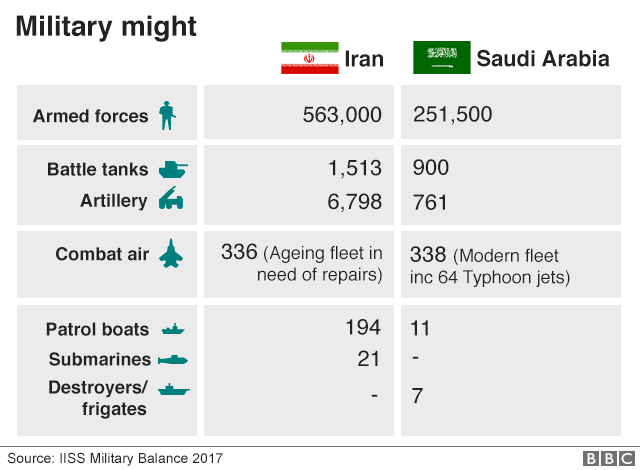
For a long time the US and its allies have seen Iran as a destabilising force in the Middle East. The Saudi leadership increasingly sees Iran as an existential threat and the crown prince seems willing to take whatever action he sees necessary, wherever he deems it necessary, to confront Tehran’s rising influence.
The danger is that Saudi Arabia’s new activism is fast making it a further source of volatility in the region.
BBC
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.