BY MARCIA DUNN
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — A strong solar storm headed toward Earth could produce northern lights in the U.S. and potentially disrupt communications this weekend.
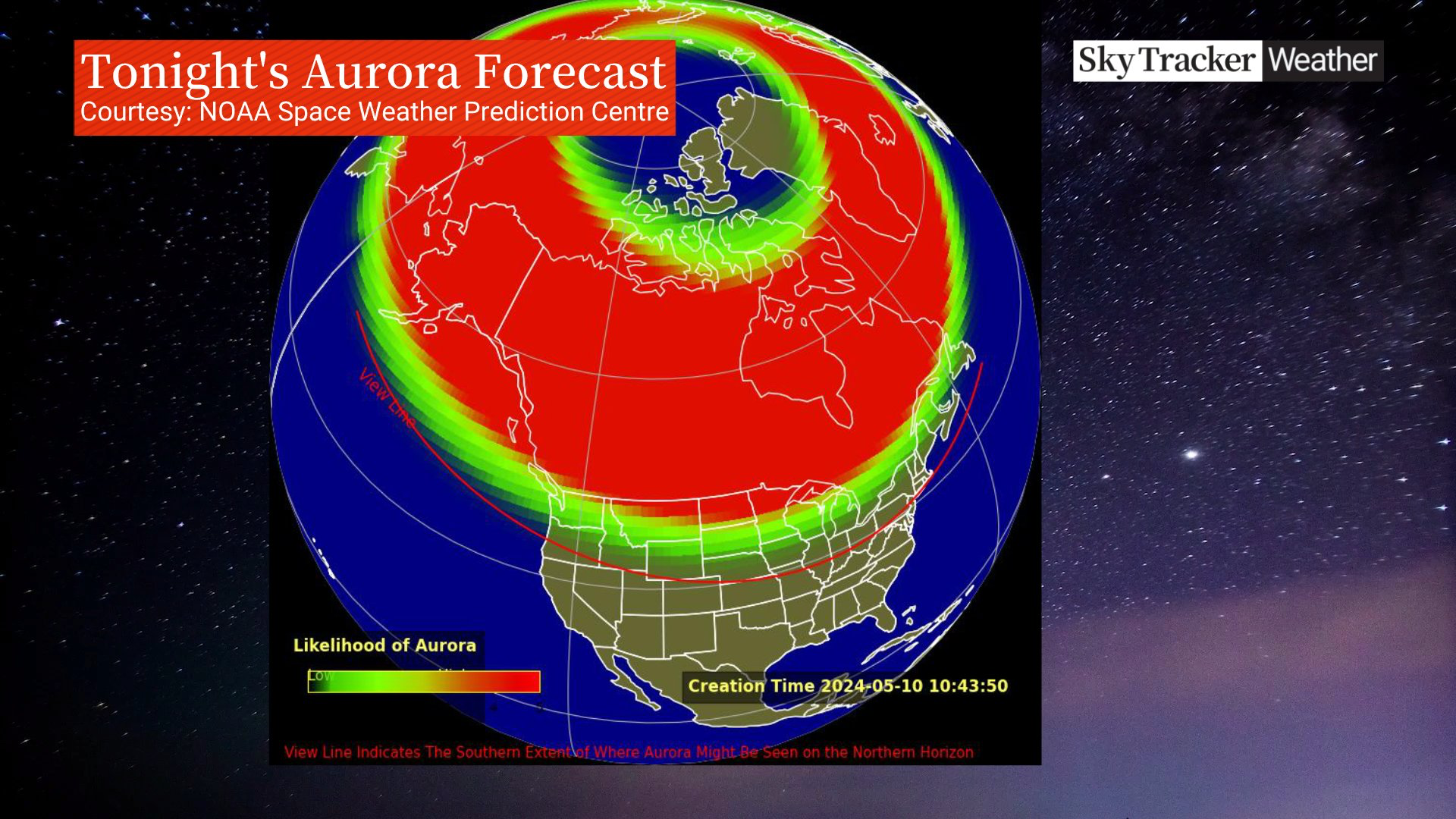
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration issued a rare geomagnetic watch — the first in nearly 20 years. The watch starts Friday and lasts all weekend.
NOAA said the sun produced strong solar flares beginning Wednesday, resulting in five outbursts of plasma capable of disrupting satellites in orbit and power grids here on Earth. Each eruption — known as a coronal mass ejection — can contain billions of tons of solar plasma.
NOAA is calling this an unusual event, pointing out that the flares seem to be associated with a sunspot that’s 16 times the diameter of Earth. An extreme geomagnetic storm in 2003 took out power in Sweden and damaged power transformers in South Africa.
The latest storm could produce northern lights as far south in the U.S. as Alabama and Northern California, according to NOAA.
Northern lights
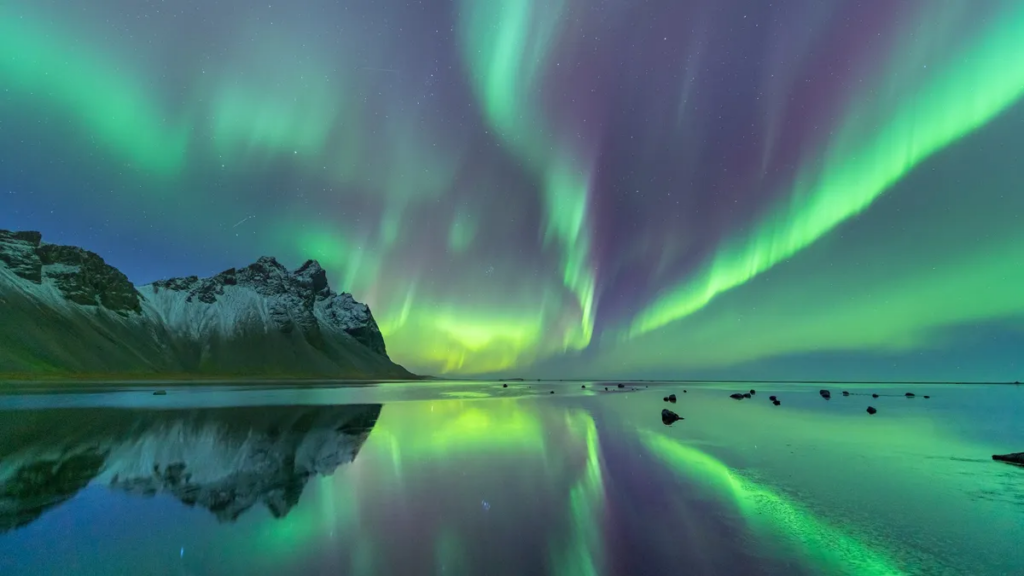

Northern lights appear as ribbons of green and purple light streaking across the sky and reflected in the water below. There are some mountains to the left side of the image. (Image credit: Chalermkiat Seedokmai via Getty Images)
The northern lights are an atmospheric phenomenon that’s regarded as the Holy Grail of skywatching.
The northern lights, or the aurora borealis, are beautiful dancing ribbons of light that have captivated people for millennia. But for all its beauty, this spectacular light show is a rather violent event.
The northern lights are created when energized particles from the sun slam into Earth’s upper atmosphere at speeds of up to 45 million mph (72 million kph), but our planet’s magnetic field protects us from the onslaught.
As Earth’s magnetic field redirects the particles toward the poles — there are southern lights, too, which you can read about below — the dramatic process transforms into a cinematic atmospheric phenomenon that dazzles and fascinates scientists and skywatchers alike.
AP

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.