BY BASSEM MROUE
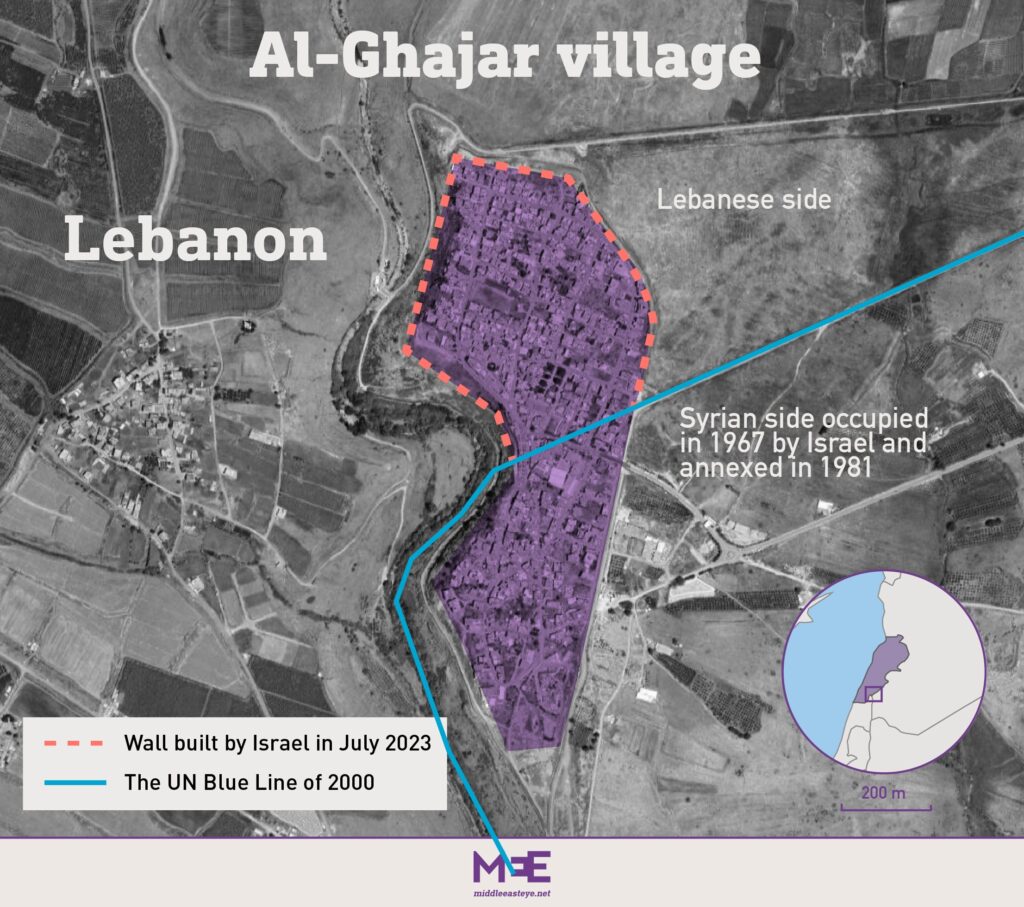
KFAR CHOUBA, Lebanon — The little village of Ghajar has been a sore point between Israel and Lebanon for years, split in two by the border between Lebanon and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights. But after a long period of calm, the dispute has begun to heat up again.
Israel has been building a wall around the half of the village in Lebanese territory, triggering condemnation from the Lebanese militiant force Hezbollah, accusing Israel of moving to annex the site. A recent exchange of fire in the area raised alarm that the dispute could trigger violence.
The growing tensions over Ghajar add to the jitters along the Lebanese-Israeli border, where Israel and Iranian-backed Hezbollah fought a destructive 34-day war in the summer of 2006. The two sides have studiously avoided outright battle ever since, despite frequent flare-ups of tension — but each constantly says a new conflict could erupt at any time.
The dispute over a small village in the green hills where Lebanon, Israel and Syria meet brings a new point of worry amid broader unrest. The West Bank has seen increased bloodshed the past week, with a major two-day offensive that Israel says targeted Palestinian militants. Within Israel, moves by the hard-right government to overhaul the judicial system have sparked large anti-government protests.
“This is Lebanese land, not Israeli,” said Lebanese shepherd Ali Yassin Diab, pointing to the half of Ghajar being enclosed by the Israeli wall as he grazed his sheep and goats nearby. Members of the U.N. peacekeeping force UNIFIL watched from a distance. In the early 2000s, Yassin used to take his herds to drink at a pond there but has since been cut off.
The village’s division is an unusual byproduct of the decades of conflict between Israel and its neighbors.
Ghajar was once part of Syria but was captured by Israel in the 1967 Mideast war as part of Syria’s Golan Heights, which Israel occupied and later annexed, with little world recognition.
In the 1980s and 1990s, Ghajar’s population expanded north into nearby Lebanese territory, held by Israel in its 18-year occupation of southern Lebanon. When Israel withdrew from Lebanon in May 2000, U.N. surveyors delineating temporary borders ruled that Ghajar’s northern part was in Lebanon, its southern part in the Golan, dividing it in two.
Six years later, Israeli troops moved into the northern part of Ghajar during the Israel-Hezbollah war. They have occupied it since and a fence was installed preventing people from entering it from Lebanon. Under the truce that ended the 2006 fighting, Israel agreed to withdraw from Ghajar, but it wanted to clinch an arrangement to keep Hezbollah from entering the village.
In a statement to the Associated Press on Friday, the Israeli Foreign Ministry said Israel recognizes the line dividing the village in 2000 but said that following the division, “Hezbollah established itself in the village” and attempted an abduction of an Israeli soldier.
Most of Ghajar’s around 3,000 residents hold Israeli nationality — some of them alongside Lebanese — and they largely identify as Syrians.
Last year, Israel started erecting a concrete wall around the northern part of the village. It also began encouraging Israeli tourism to the village. In its statement, the foreign ministry said that the wall “is on the same route as the fence that was in place before” around the village.
In apparent reply to the near finishing of the wall, Hezbollah set up two tents nearby, including one in the area of Chebaa Farms, which both Israel and Lebanon claim as its territory. It is not clear what is inside the tents.
Israel filed a complaint with the United Nations, claiming the tents were several dozen meters (yards) inside of Israeli territory. Hezbollah says the tents are in Lebanese territory.
On Monday, UNIFIL’s commander relayed an Israeli request to Lebanon’s caretaker prime minister and parliament speaker to remove the tent. They responded that Israel should withdraw its troops from the Lebanese part of Ghajar, according to Lebanese Foreign Minister Abdallah Bouhabib.
Associated Press


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.